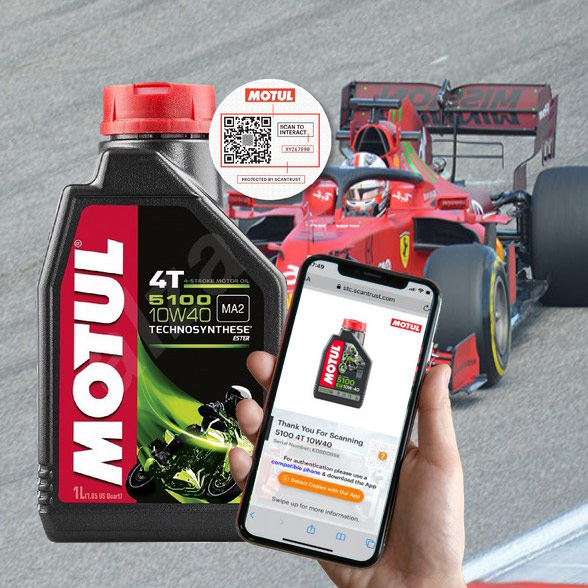
In the past decade of working with brands to get QR codes on packaging we’ve seen it all. Products big, small, curved, metal, flexible – at every step of the way there are key nuances to getting QR codes “right”. This guide shares our accumulated insight for putting QR codes on product packaging, covering best practices for designing, printing, and implementing them for various product types and use cases.
Brand Guide: QR Codes on Packaging
After helping global brands label billions of consumer and industrial goods with QR codes, we've collected our best tips and tricks in one place to help make your QR code projects more successful.

Introduction
QR code size and placement guidelines
The size and placement of your QR code significantly impact its effectiveness. Follow these guidelines to ensure your QR code is easily scannable.
- We recommend a minimum QR code size of 1cm by 1cm. Anything between 1cm x 1cm and 2cm x 2cm is workable. With improvements in QR code scanning technology, the old standard of 2cm x 2cm is outdated.
- Place the QR code in a prominent location. Choose a location that is easily visible, accessible, and scannable to the end user.
- Leave sufficient whitespace or “quiet zone. Maintain a sufficient ‘quiet zone’ around the QR code to prevent scanning issues. This space helps the scanner distinguish the QR code from surrounding elements. Your QR code generator should do this for you.

QR code color and contrast guidelines
While QR codes can have different colors and shapes, you should ensure a strong contrast between the QR code and its background. Dark QR codes on light backgrounds (or vice versa) work best.
Black and white QR codes are the gold standard for ease of scanning by a variety of different devices in different environments and lighting settings.
Inverted colors can be appealing but not all QR code readers can read them:

How to place icons in QR Codes
Adding logos or graphics to the center of a QR code can enhance branding, but it must be done carefully to ensure the code remains scannable. Here are four pointers to do so:
- Keep the logo small: The logo or graphic should be small enough not to obstruct the key patterns of the QR code. Position it centrally but ensure it does not cover the three corner squares, which are crucial for scanning.
- Maintain contrast: Ensure that the logo or graphic contrasts well with the QR code to prevent confusion during scanning. A dark logo on a light QR code background or vice versa is ideal.
- Use a higher error correction level: Utilize high error correction levels (up to 30%) when generating the QR code. This allows for more of the QR code to be obscured while still being scannable. Your QR code generator should do this for you dynamically if a logo is added.
- Test the QR code: After adding graphics, test the QR code with multiple scanning apps and devices, and in different lighting conditions, to confirm that it remains functional.
QR codes under the cap
Placement under the cap: Some brands use “under the cap” QR codes to measure if a product has been consumed, which makes for a stronger loyalty program. These may incur costs and special processes.
QR code on a curved surface
For placement of QR codes on products or surfaces which are curved, keep in mind that distortion caused by the curvature may impact ease of scanning of the QR code. Your QR code solution provider can provide guidance on this.

Using QR codes on consumer products
For consumer products, the primary use cases often include providing product information, promotional offers, and customer engagement opportunities.
Placement: QR codes should be prominently displayed on the front or top of the packaging, where they are most visible and accessible. This encourages consumers to scan them while making a purchase decision.
Calls to Action: If targeting a use case with consumers, use clear and enticing calls to action (e.g., “Scan for a special offer!”) to motivate the consumer to engage with the QR code.
Example of QR codes for consumer products: Ferrara candy uses Scantrust QR codes for GMO ingredient disclosure.
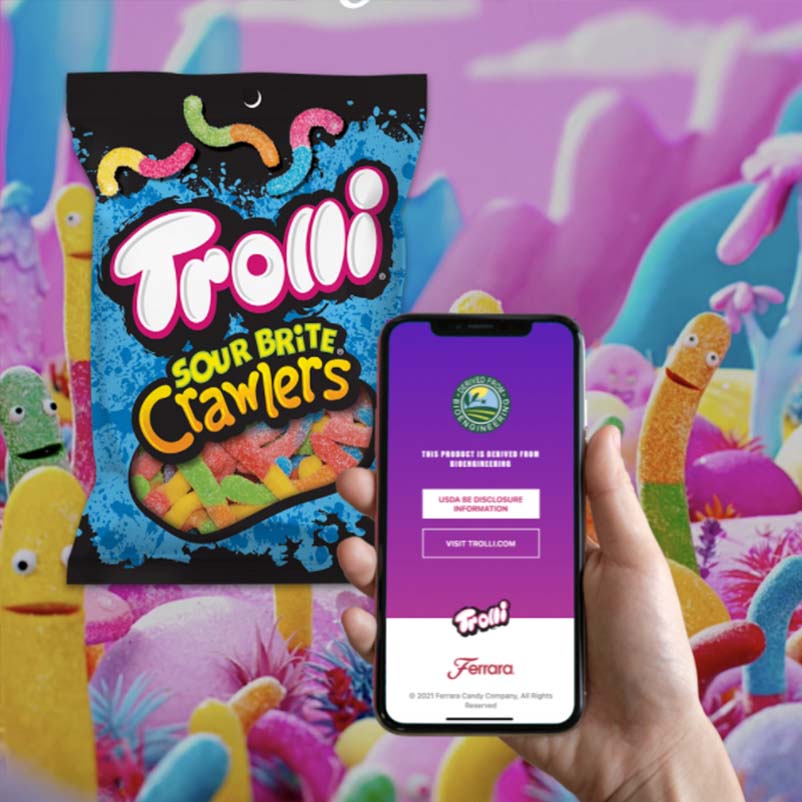

See case study
Using QR codes on industrial products
For industrial products, QR codes can provide operational instructions, maintenance guides, and safety information. But these QR codes may be subject to more wear-and-tear, or may need to satisfy multiple use cases.
Ensure that the QR codes can withstand wear and tear given the anticipated use case and environment. QR codes are increasingly lasered onto surfaces for industrial use cases.
Consider all use cases for placement; QR codes should be prominently displayed where both end-users and scanning equipment within the supply chain can reach it, depending on the QR code’s use case. This is particularly important if the codes are serialized and/or are being used for traceability. Consider if they are scannable during product operation or maintenance, ensuring they do not interfere with critical information or controls.
Example of QR codes for industrial products: VARTA uses QR codes for automotive battery traceability

See case study
Printing technology and QR codes
The success of your QR code also depends on the printing method and materials used. Consider the following factors when preparing your QR codes for printing:
Digital printing QR codes: This method allows for quick turnaround times and the ability to print variable data, making it ideal for small batches or customized QR codes. However, challenges include ensuring consistent quality across prints and potential issues with color fidelity. Digital printing can also be slower for larger runs compared to offset printing.
Analog printing QR codes: Offset or flexo are two common analog printing methods. These are known for producing high-quality prints at a faster speed for large volumes compared to digital printing. However, they are usually not suitable for variable data printing. scannability.
Hybrid printing QR codes: Involves both digital and offset printing.
Lasering QR codes: QR codes are increasingly being lasered onto plastic and metal surfaces. Lasering is particularly appealing for use cases on mechanical parts, such as in automotive or industrial applications, where wear and tear from usage would damage a printed or sticker-based QR code to the extent that it would no longer be scannable.
Key considerations for printing QR codes
- Choose materials that will not result in QR code bleed and will not interfere with scanning, such as reflective surfaces or textures that may distort the code.
- Use vector formats for the QR code file, if possible
- Ensure high-quality printing to maintain code clarity and ease of scanning. Test your QR codes before mass printing to confirm they function correctly.
- Consider the print speed requirements; digital printing is generally slower for larger runs but faster for small batches, while offset printing is efficient for high-volume orders but less flexible for customization.
Printer integration and workflow tools of your QR code provider: For many brands and use cases, it’s not feasible to download a new batch of QR codes and email it to a printer each time. Your enterprise QR code solution provider should provide printer integration APIs and QR code work order tools.
QR code resolution requirements
Ensure the QR code is high-resolution and free from blurriness. This requires a high-quality image of the QR code and sufficient printing DPI.
File format: Vector formats are preferable as they maintain quality across various sizes and mediums.
Printing: While 300dpi is typically recommended as the standard, some substrates or surfaces may bleed. You should always test your printed codes.
Printing serialized QR codes
Serialization, the process of assigning unique identifiers to individual products, can be effectively integrated with QR codes to enhance product traceability and security. Because each QR code is unique, they open up many other use cases, including supply chain traceability, product authentication, and the ability to run loyalty programs or other marketing campaigns.
Serialization requires digital or hybrid printing and often requires specialized equipment, such as inline scanners, installed on the production line.
How to print GS1 Digital Link QR codes
Brands are increasingly printing QR codes compatible with GS1 Digital Link, an emerging standard. This standard allows for the encoding of product information, including serial numbers, into a single QR code and linking that QR code and product (SKU or unit) to information online.
GS1 Digital Link ensures that QR codes can be scanned by various devices and applications, providing a seamless experience for consumers. It’s goal is to enhance data sharing, interoperability, and make QR codes more suitable for use in compliance use cases.
Your QR code generator needs to be compatible with GS1 Digital Link and provide a way for you to associate the codes with the GS1 identifiers. Besides that, there are no special printing requirements for GS1 Digital Link QR codes.
Testing QR codes after printing
Before launching your QR code campaign, thorough testing is crucial to ensure functionality and performance.
Always test your QR codes on various devices and in different lighting conditions to confirm they work properly. This includes checking from different locations.
Ensure that the URLs embedded in your QR codes lead to mobile-optimized pages that load quickly. Slow-loading pages can deter users from engaging further. One of the biggest issues we help customers with is ensuring that QR code content delivery is optimized for all regions where QR codes are intended to be used.
Lastly, you should test that the QR codes, when scanned, are generating the expected data in the associated tracking tools. For example, if using them for supply chain traceability or marketing, check that the scan data appears correctly in the relevant dashboards.
Conclusion: Time to print your QR codes!
QR codes can be invaluable for brands – but only if they’re printed properly. The process is manageable with the right guidelines and of course, a great partner to guide you.
Looking for an enterprise QR code solution for your brands? One of our experts is more than happy to share insight honed from printing QR codes on billions of products worldwide for over a decade.
